Witness a rare cosmic event this October: Twin comets Swan and Lemmon align with Orionid meteor shower |
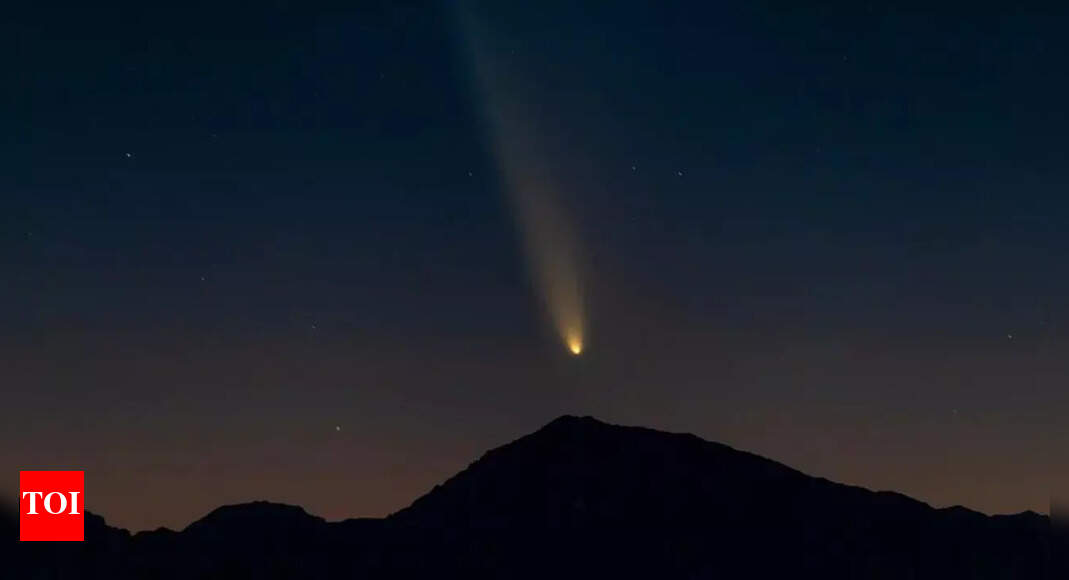

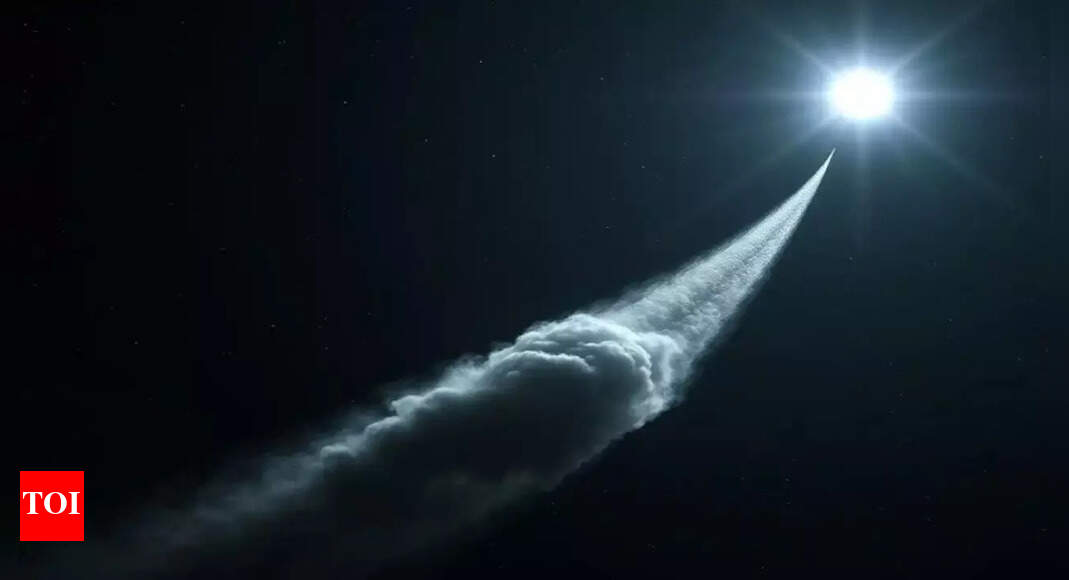
This October, skywatchers have a rare celestial show to look forward to as Comet SWAN (C/2025 R2) and Comet Lemmon (C/2025 A6) approach their closest point to Earth around October 21. Observers in the Northern Hemisphere may be able to see both comets in the sky on the same night, a spectacular and uncommon sight. The event perfectly aligns with the peak of the Orionid meteor shower and a new moon, offering exceptionally dark skies for optimal viewing. SWAN will glow low in the southwestern sky while Lemmon moves across the northwestern horizon, making binoculars helpful. Together, the twin comets and streaking meteors promise one of the most memorable astronomical displays of 2025.
Rare double comet sighting as Swan and Lemmon brighten October skies
This October marks a rare opportunity to view not just one, but two bright comets within days of each other. Comet SWAN and Comet Lemmon are expected to become visible in dark skies, potentially even without telescopes, though binoculars may enhance the experience.The visibility of comets is notoriously unpredictable, as they can brighten or fade rapidly due to sudden outbursts. Both comets will begin appearing in the sky around October 9, but October 21 is the prime night for viewing due to minimal moonlight and the peak of the Orionid meteor shower.
When and where to spot comet SWAN
Discovered in September 2025, the blueish-green Comet SWAN (C/2025 R2) is expected to be visible to observers at mid-northern latitudes starting the second week of October. The comet will appear low in the southwestern sky in the constellation Libra shortly after sunset.As October progresses, SWAN will move northeast through Scorpius, Ophiuchus, and Serpens, gradually climbing higher in the sky. By October 13, it will pass just below Sabik, a bright star in Ophiuchus. Its peak brightness is anticipated around October 21, when it reaches its closest point to the Sun, before gradually dimming as it moves away from Earth.For optimal viewing, astronomers recommend heading to locations with minimal light pollution, such as Dark Sky Parks or areas with unobstructed western horizons.
Tracking comet Lemmon: Brightening across the northwestern sky
Comet Lemmon (C/2025 A6), discovered earlier in January 2025 by the Mount Lemmon Survey in Arizona, has been steadily brightening as it approaches Earth. By mid-October, it becomes visible low in the northwestern sky, moving beneath the Big Dipper constellation.Around October 16, Lemmon will pass within a degree of Cor Caroli, the bright star in Canes Venatici, offering a perfect reference point for skywatchers. Like SWAN, Lemmon will reach its closest approach to Earth on October 21, making this night ideal for observing both celestial visitors.
Orionid meteor shower peaks alongside comets in October
Adding to the spectacle, the Orionid meteor shower will peak on October 21-22, offering around 20 meteors per hour under clear, dark skies. Best observed after midnight when Orion rises high in the southeast, these meteors originate from debris left behind by Halley’s Comet.The alignment of events this year is exceptional: the new moon ensures dark skies, while the simultaneous presence of Comet SWAN and Comet Lemmon provides stargazers with a rare, multi-layered celestial display. Shooting stars and twin comets in one night make this an unmissable event for astronomy enthusiasts and casual skywatchers alike.
Best tips for observing the October celestial show
To maximise your viewing experience, experts suggest finding a location away from city lights, with clear western and northern horizons for observing the comets. Bringing binoculars is advisable, as comet brightness can vary. Documenting the event with a camera or smartphone tripod is also recommended for capturing the fleeting beauty of both comets and the meteor shower.October 21 promises a once-in-a-lifetime astronomical spectacle, where enthusiasts can witness Comet SWAN, Comet Lemmon, and the Orionids all in one breathtaking night sky show.Also Read | The Red Sea vanished from Earth for 100,000 years: What brought it back will astonish you